A research work using NLP techniques on the Yelp dataset.
This project was created for a Master's course in Natural Language Processing at Cal Poly. The GitHub repo is available here.
The motivation behind this project is to identify the topics of a Yelp customer review and determine the sentiment (positive, negative, or neutral) of each topic.

Implementation
The task is to analyze and summarize the categories and sentiment of a review. A review is analyzed per sentence. (We assume that a single sentence has an overall topic and sentiment.) The proposed topic-sentiment system is a combination of two parts:
- Topic Classification: Identify the topics mentioned in a review
- Sentiment Analysis: Determine the sentiment for each topic in a review
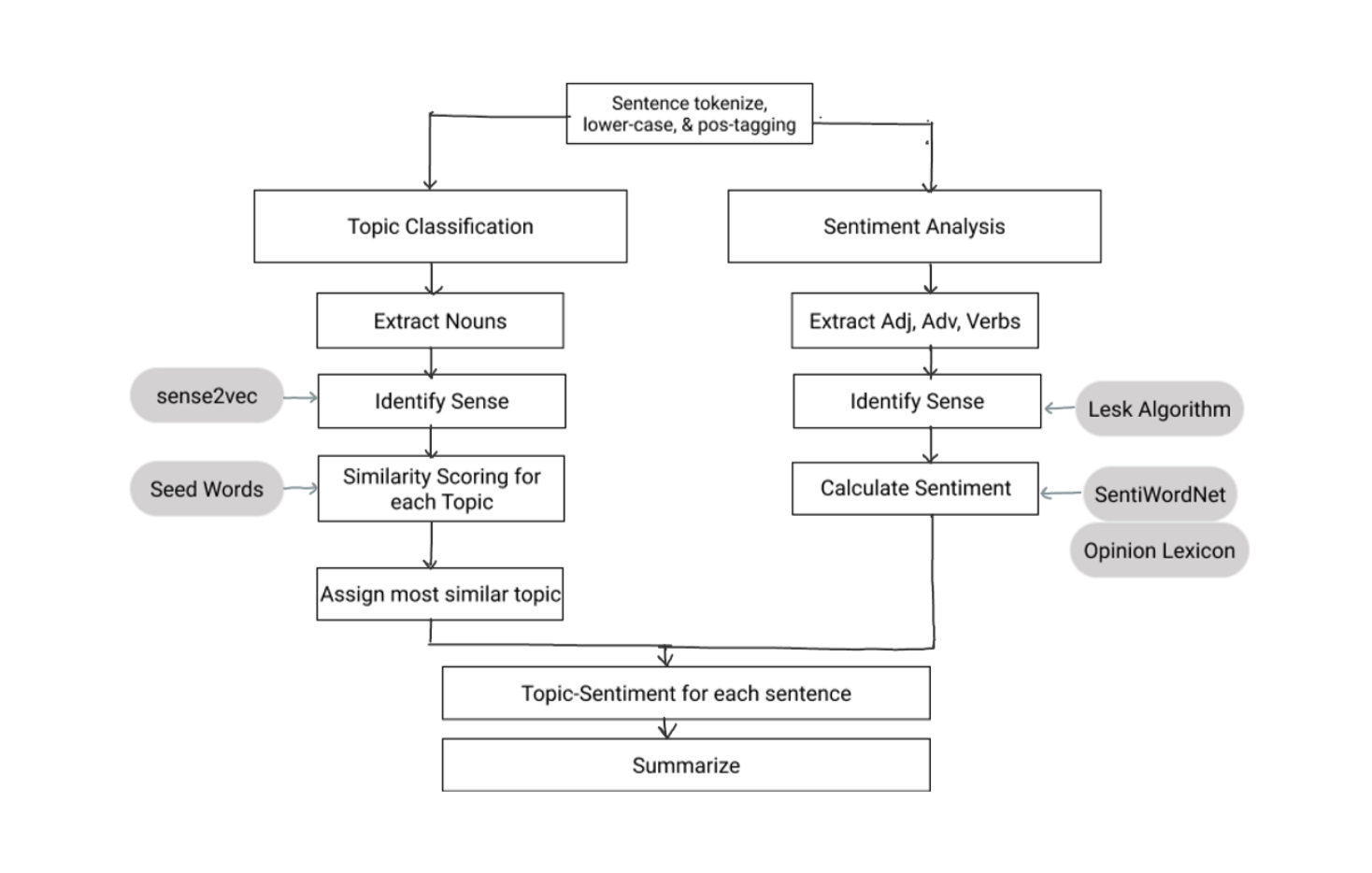
Topic Classification Algorithm
The topic of a sentence is usually indicated by a noun, so we analyze all potential nouns and determine which topic they are most similar to. Similarity is calculated by using word embeddings and a set of seed words per category. Word sense disambiguation is handled using sense2vec's algorithm.
# global variables
seeds['food']= "food drink"
seeds['atms']= "atmosphere place environment"
seeds['serv']= "server management time"
seeds['prce']= "money expensive"
def topicClassification(text, seed words, category=['food', 'atms', 'serv', 'prce']):
# split into sentences
preprocess(text)
all_topics = []
for sentence in sentences:
nouns = get_nouns(sentence)
topic = max(categorize(seeds[cat], nouns) for each category)
all_topics.add(topic)
topic_scores = group together similar topics and sum similarity scores
return topic_scores
def categorize(seeds, nouns):
# compute each nouns' similarity to each seed using vectors
scores = {}
for noun in nouns:
score_per_seed = []
scores[noun] = max(similarity(noun, seed) for seed in seeds)
return scores
Sentiment Analysis Algorithm
Sentiment is usually indicated through opinion words, such as adjectives, adverbs, and verbs; so, we only calculate the sentiment of those words. Word sense disambiguation is handled using NLTK's implementation of the Lesk algorithm.
def sentimentAnalysis(sentence, included_pos=[wordnet.ADJ, wordnet.ADV,
wordnet.VERB]):
# sum the total sentiment score
total_sent = 0
total_toks = 0
for word in sentence:
if word.tag not in included_pos: continue
# use the common sense of each word
common_sense = lesk(sentence, word, wntag)
# calculate the sentiment of this sense, add to total
total_sent += calculate_sentiment(commone_sense)
# calculate average sentiment
avg_sent = total_sent/total_toks
return avg_sent
def calculate_sentiment(name):
global NEG_WORDS, POS_WORDS
syn = senti_synset(name)
pos,neg,obj = syn.pos_score(), syn.neg_score(), syn.obj_score()
# Use Hu and Liu's lexicon to determine orientation (if applicable)
if name in NEG_WORDS:
return neg
elif name in POS_WORDS:
return pos
# prune objective words
if obj > 0.8:
return 0.0
# words aren't indicated as pos/neg by Hu&Liu's lexicon
# so return the difference of both scores
return pos-neg